Preventing Blockchain Analysis: Best Practices
Learn how to protect your cryptocurrency transactions from blockchain analysis tools, implement privacy best practices, and maintain transaction anonymity.

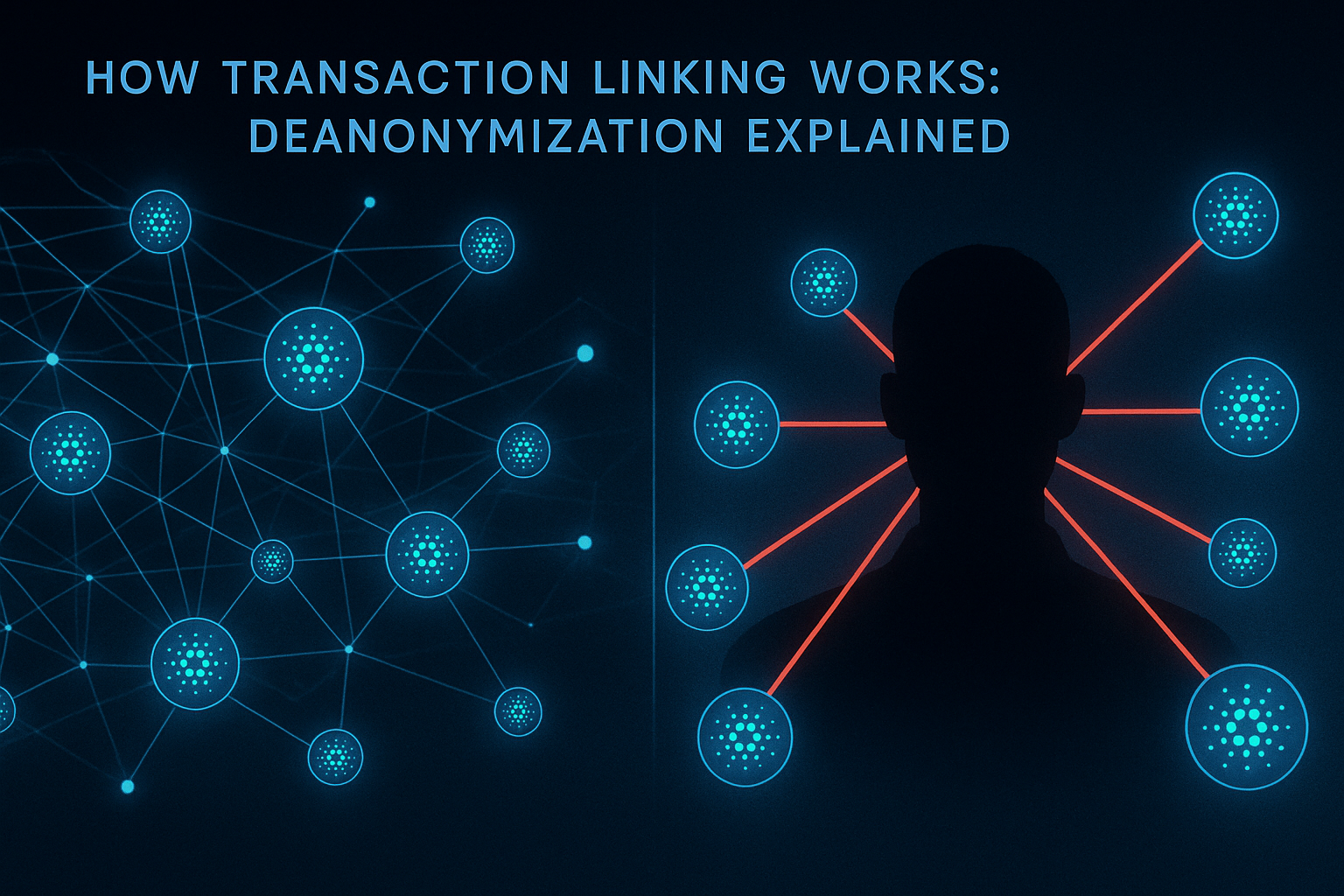
Understanding Blockchain Analysis
Blockchain analysis has become increasingly sophisticated, with companies developing powerful tools to trace cryptocurrency transactions and identify users. Understanding how these tools work is the first step in protecting your privacy.
Modern blockchain analysis combines multiple techniques including transaction graph analysis, behavioral pattern recognition, and machine learning algorithms to identify users and trace transaction flows. These tools can link addresses to real-world identities and reveal spending patterns.
Common Analysis Techniques
Blockchain analysts use several techniques to identify users and trace transactions:
- Address Clustering: Grouping addresses controlled by the same entity
- Transaction Graph Analysis: Analyzing transaction patterns and relationships
- Timing Analysis: Correlating transactions based on timing
- Amount Correlation: Linking transactions based on unique amounts
- Behavioral Analysis: Identifying patterns in user behavior
"The best defense against blockchain analysis is understanding how it works and implementing multiple layers of privacy protection."
Address Management Best Practices
Proper address management is crucial for maintaining privacy. Poor address management is one of the most common ways users compromise their privacy.
Address Reuse Prevention
Never reuse addresses for multiple transactions:
- Generate a new address for each transaction
- Use hierarchical deterministic (HD) wallets
- Implement address rotation strategies
- Monitor address usage patterns
Address Generation Strategies
Use multiple independent address generation methods:
- Multiple seed phrases
- Different wallet software
- Hardware wallet integration
- Cross-platform address creation
Transaction Pattern Obfuscation
Avoiding predictable transaction patterns is essential for maintaining privacy. Analysts use pattern recognition to identify users and link transactions.
Timing Randomization
Vary the timing of your transactions to prevent timing analysis:
- Use random delays between transactions
- Avoid predictable transaction schedules
- Implement time-based obfuscation
- Consider timezone variations
Amount Obfuscation
Make transaction amounts less identifiable:
- Avoid round numbers
- Use psychologically appealing amounts
- Implement amount randomization
- Consider amount splitting strategies
Mixing and Privacy Services
Regular use of mixing services is one of the most effective ways to protect your privacy. However, choosing the right mixing service is crucial.
Choosing Mixing Services
Select mixing services based on several criteria:
- Reputation: Choose well-established services
- Security: Look for strong security practices
- Privacy: Verify privacy guarantees
- Transparency: Prefer open-source solutions
Mixing Strategies
Implement effective mixing strategies:
- Mix coins regularly
- Use different mixing services
- Implement multi-hop mixing
- Vary mixing amounts and timing
Network-Level Privacy
Network-level privacy is often overlooked but is crucial for preventing IP-based identification and traffic analysis.
Tor Integration
Always use Tor or similar anonymization networks:
- Route all cryptocurrency traffic through Tor
- Use Tor hidden services when available
- Implement automatic Tor routing
- Monitor for IP leaks
VPN and Proxy Services
Additional network privacy measures:
- Use reputable VPN services
- Implement proxy chains
- Rotate network connections
- Monitor for DNS leaks
Operational Security
Operational security (OPSEC) is crucial for maintaining privacy. Poor OPSEC can compromise even the strongest technical privacy measures.
Information Security
Protect sensitive information:
- Never share private keys or seed phrases
- Use secure communication channels
- Implement proper key management
- Regularly update security practices
Behavioral Security
Maintain consistent privacy practices:
- Follow established procedures
- Avoid predictable behaviors
- Implement security checklists
- Regular security audits
Advanced Privacy Techniques
Advanced users can implement sophisticated privacy techniques to achieve maximum anonymity.
CoinJoin Protocols
Use CoinJoin and similar protocols:
- Participate in CoinJoin transactions
- Use decentralized mixing protocols
- Implement peer-to-peer mixing
- Join mixing pools
Privacy Coins
Consider using privacy-focused cryptocurrencies:
- Monero for built-in privacy
- Zcash for selective privacy
- Dash for optional privacy
- Other privacy coins
Wallet Security
Secure wallet management is essential for maintaining privacy and preventing theft.
Hardware Wallets
Use hardware wallets for maximum security:
- Store private keys offline
- Use multiple hardware wallets
- Implement backup strategies
- Regular security updates
Software Wallet Security
Secure software wallet usage:
- Use reputable wallet software
- Keep software updated
- Implement proper backups
- Use secure devices
Monitoring and Detection
Regular monitoring helps detect privacy leaks and security issues before they become serious problems.
Transaction Monitoring
Monitor your transactions for privacy leaks:
- Check for address reuse
- Monitor transaction patterns
- Verify mixing effectiveness
- Detect analysis attempts
Security Audits
Regular security audits help maintain privacy:
- Review privacy practices
- Test security measures
- Update procedures
- Identify vulnerabilities
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
Privacy practices must be balanced with legal and regulatory requirements.
Compliance Requirements
Understand applicable regulations:
- Anti-money laundering (AML) laws
- Know-your-customer (KYC) requirements
- Tax reporting obligations
- International regulations
Privacy vs. Compliance
Balance privacy with compliance:
- Legitimate privacy use cases
- Compliance-friendly practices
- Documentation requirements
- Legal consultation
Future-Proofing Privacy
As blockchain analysis becomes more sophisticated, privacy practices must evolve to maintain effectiveness.
Emerging Threats
Stay informed about new analysis techniques:
- Machine learning analysis
- Advanced pattern recognition
- Cross-chain analysis
- Metadata correlation
Adaptive Strategies
Implement adaptive privacy strategies:
- Regular practice updates
- New technology adoption
- Threat assessment
- Continuous improvement
Common Privacy Mistakes
Avoiding common privacy mistakes is crucial for maintaining anonymity.
Technical Mistakes
Common technical privacy mistakes:
- Address reuse
- Predictable patterns
- Poor mixing practices
- Network privacy failures
Operational Mistakes
Common operational privacy mistakes:
- Information sharing
- Predictable behaviors
- Poor security practices
- Compliance failures
Preventing blockchain analysis requires a comprehensive approach that combines technical measures with operational security. By understanding how analysis works and implementing multiple layers of privacy protection, users can significantly improve their anonymity and protect their financial privacy.